一个 Python 3 库,用于以编程方式生成 SVG 图像(矢量图)并渲染它们或在 Jupyter 笔记本中显示它们
项目描述
绘制Svg
一个 Python 3 库,用于以编程方式生成 SVG 图像(矢量图)并渲染它们或在 Jupyter 笔记本中显示它们。
DrawableBasicElement支持大多数常见的 SVG 标签,并且可以通过编写or的一个小子类轻松添加其他标签DrawableParentElement。
包含一个交互式Jupyter 笔记本小部件 ,drawSvg.widgets.DrawingWidget它可以根据鼠标事件更新绘图。
安装
drawSvg 在 PyPI 上可用:
$ pip3 install drawSvg
先决条件
Cairo 需要单独安装。安装 Cairo 后,drawSvg 可以输出除 SVG 之外的 PNG 或其他图像格式。请参阅Cairo 中针对 Linux、Windows 和 macOS 的平台特定说明。下面是在 Linux 发行版和 macOS 上安装 Cairo 的一些示例。
Ubuntu
$ sudo apt-get install libcairo2
苹果系统
使用自制软件:
$ brew install cairo
例子
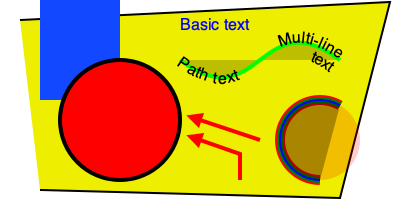
基本绘图元素
import drawSvg as draw
d = draw.Drawing(200, 100, origin='center', displayInline=False)
# Draw an irregular polygon
d.append(draw.Lines(-80, -45,
70, -49,
95, 49,
-90, 40,
close=False,
fill='#eeee00',
stroke='black'))
# Draw a rectangle
r = draw.Rectangle(-80,0,40,50, fill='#1248ff')
r.appendTitle("Our first rectangle") # Add a tooltip
d.append(r)
# Draw a circle
d.append(draw.Circle(-40, -10, 30,
fill='red', stroke_width=2, stroke='black'))
# Draw an arbitrary path (a triangle in this case)
p = draw.Path(stroke_width=2, stroke='lime',
fill='black', fill_opacity=0.2)
p.M(-10, 20) # Start path at point (-10, 20)
p.C(30, -10, 30, 50, 70, 20) # Draw a curve to (70, 20)
d.append(p)
# Draw text
d.append(draw.Text('Basic text', 8, -10, 35, fill='blue')) # Text with font size 8
d.append(draw.Text('Path text', 8, path=p, text_anchor='start', valign='middle'))
d.append(draw.Text(['Multi-line', 'text'], 8, path=p, text_anchor='end'))
# Draw multiple circular arcs
d.append(draw.ArcLine(60,-20,20,60,270,
stroke='red', stroke_width=5, fill='red', fill_opacity=0.2))
d.append(draw.Arc(60,-20,20,60,270,cw=False,
stroke='green', stroke_width=3, fill='none'))
d.append(draw.Arc(60,-20,20,270,60,cw=True,
stroke='blue', stroke_width=1, fill='black', fill_opacity=0.3))
# Draw arrows
arrow = draw.Marker(-0.1, -0.5, 0.9, 0.5, scale=4, orient='auto')
arrow.append(draw.Lines(-0.1, -0.5, -0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 0, fill='red', close=True))
p = draw.Path(stroke='red', stroke_width=2, fill='none',
marker_end=arrow) # Add an arrow to the end of a path
p.M(20, -40).L(20, -27).L(0, -20) # Chain multiple path operations
d.append(p)
d.append(draw.Line(30, -20, 0, -10,
stroke='red', stroke_width=2, fill='none',
marker_end=arrow)) # Add an arrow to the end of a line
d.setPixelScale(2) # Set number of pixels per geometry unit
#d.setRenderSize(400,200) # Alternative to setPixelScale
d.saveSvg('example.svg')
d.savePng('example.png')
# Display in Jupyter notebook
d.rasterize() # Display as PNG
d # Display as SVG
渐变
import drawSvg as draw
d = draw.Drawing(1.5, 0.8, origin='center')
d.draw(draw.Rectangle(-0.75,-0.5,1.5,1, fill='#ddd'))
# Create gradient
gradient = draw.RadialGradient(0,-0.35,0.7*10)
gradient.addStop(0.5/0.7/10, 'green', 1)
gradient.addStop(1/10, 'red', 0)
# Draw a shape to fill with the gradient
p = draw.Path(fill=gradient, stroke='black', stroke_width=0.002)
p.arc(0,-0.35,0.7,30,120)
p.arc(0,-0.35,0.5,120,30,cw=True, includeL=True)
p.Z()
d.append(p)
# Draw another shape to fill with the same gradient
p = draw.Path(fill=gradient, stroke='red', stroke_width=0.002)
p.arc(0,-0.35,0.75,130,160)
p.arc(0,-0.35,0,160,130,cw=True, includeL=True)
p.Z()
d.append(p)
# Another gradient
gradient2 = draw.LinearGradient(0.1,-0.35,0.1+0.6,-0.35+0.2)
gradient2.addStop(0, 'green', 1)
gradient2.addStop(1, 'red', 0)
d.append(draw.Rectangle(0.1,-0.35,0.6,0.2,
stroke='black', stroke_width=0.002,
fill=gradient2))
# Display
d.setRenderSize(w=600)
d
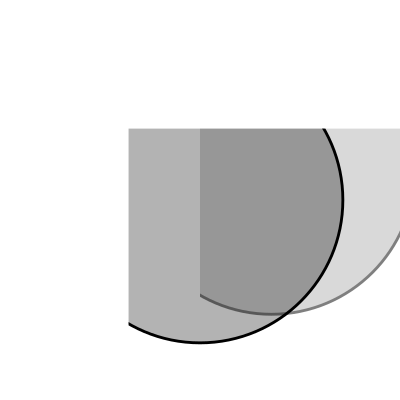
重复的几何图形和剪辑路径
import drawSvg as draw
d = draw.Drawing(1.4, 1.4, origin='center')
# Define clip path
clip = draw.ClipPath()
clip.append(draw.Rectangle(-.25,.25-1,1,1))
# Draw a cropped circle
c = draw.Circle(0,0,0.5, stroke_width='0.01', stroke='black',
fill_opacity=0.3, clip_path=clip,
id='circle')
d.append(c)
# Make a transparent copy, cropped again
g = draw.Group(opacity=0.5, clip_path=clip)
g.append(draw.Use('circle', 0.25,0.1))
d.append(g)
# Display
d.setRenderSize(400)
d.rasterize()
实现其他 SVG 标签
import drawSvg as draw
# Subclass DrawingBasicElement if it cannot have child nodes
# Subclass DrawingParentElement otherwise
# Subclass DrawingDef if it must go between <def></def> tags in an SVG
class Hyperlink(draw.DrawingParentElement):
TAG_NAME = 'a'
def __init__(self, href, target=None, **kwargs):
# Other init logic...
# Keyword arguments to super().__init__() correspond to SVG node
# arguments: stroke_width=5 -> stroke-width="5"
super().__init__(href=href, target=target, **kwargs)
d = draw.Drawing(1, 1.2, origin='center')
# Create hyperlink
hlink = Hyperlink('https://www.python.org', target='_blank',
transform='skewY(-30)')
# Add child elements
hlink.append(draw.Circle(0,0,0.5, fill='green'))
hlink.append(draw.Text('Hyperlink',0.2, 0,0, center=0.6, fill='white'))
# Draw and display
d.append(hlink)
d.setRenderSize(200)
d
带有 SVG Animate 标签的动画
import drawSvg as draw
d = draw.Drawing(200, 200, origin='center')
# Animate the position and color of circle
c = draw.Circle(0, 0, 20, fill='red')
# See for supported attributes:
# https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/SVG/Element/animate
c.appendAnim(draw.Animate('cy', '6s', '-80;80;-80',
repeatCount='indefinite'))
c.appendAnim(draw.Animate('cx', '6s', '0;80;0;-80;0',
repeatCount='indefinite'))
c.appendAnim(draw.Animate('fill', '6s', 'red;green;blue;yellow',
calcMode='discrete',
repeatCount='indefinite'))
d.append(c)
# Animate a black circle around an ellipse
ellipse = draw.Path()
ellipse.M(-90, 0)
ellipse.A(90, 40, 360, True, True, 90, 0) # Ellipse path
ellipse.A(90, 40, 360, True, True, -90, 0)
ellipse.Z()
c2 = draw.Circle(0, 0, 10)
# See for supported attributes:
# https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/SVG/Element/animateMotion
c2.appendAnim(draw.AnimateMotion(ellipse, '3s',
repeatCount='indefinite'))
# See for supported attributes:
# https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/SVG/Element/animateTransform
c2.appendAnim(draw.AnimateTransform('scale', '3s', '1,2;2,1;1,2;2,1;1,2',
repeatCount='indefinite'))
d.append(c2)
d.saveSvg('animated.svg') # Save to file
d # Display in Jupyter notebook
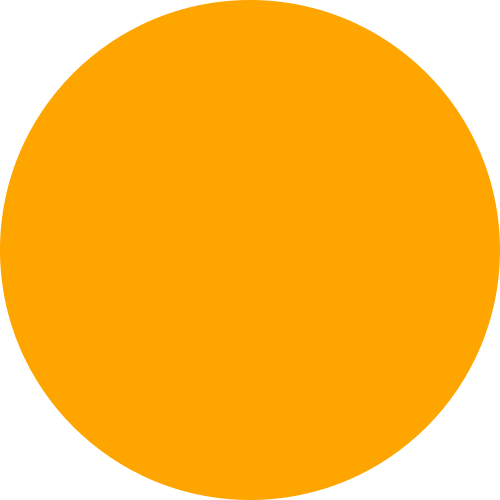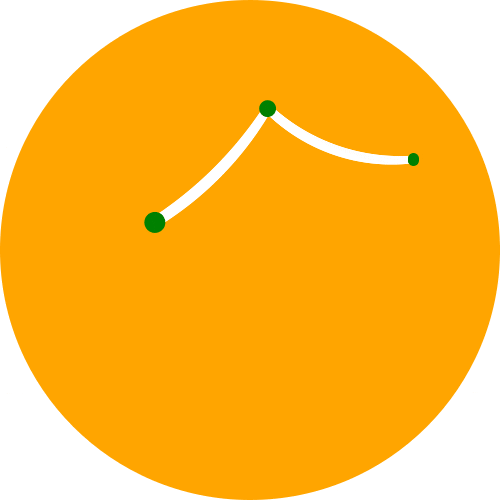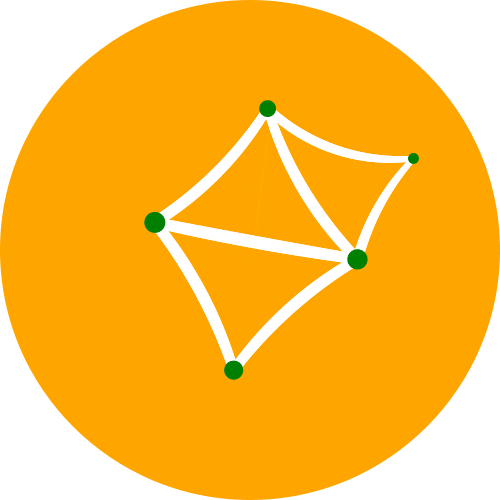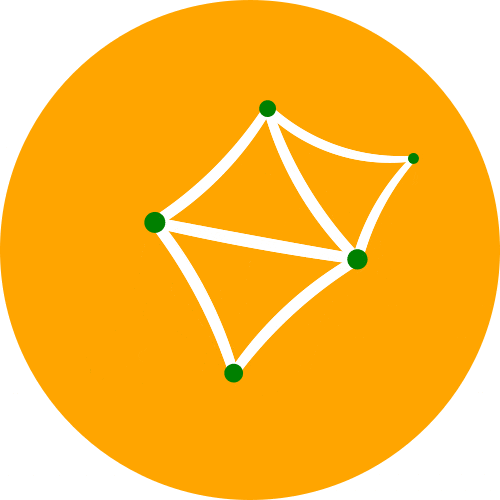
交互式小部件
import drawSvg as draw
from drawSvg.widgets import DrawingWidget
import hyperbolic.poincare.shapes as hyper # pip3 install hyperbolic
# Create drawing
d = draw.Drawing(2, 2, origin='center')
d.setRenderSize(500)
d.append(draw.Circle(0, 0, 1, fill='orange'))
group = draw.Group()
d.append(group)
# Update the drawing based on user input
click_list = []
def redraw(points):
group.children.clear()
for x1, y1 in points:
for x2, y2 in points:
if (x1, y1) == (x2, y2): continue
p1 = hyper.Point.fromEuclid(x1, y1)
p2 = hyper.Point.fromEuclid(x2, y2)
if p1.distanceTo(p2) <= 2:
line = hyper.Line.fromPoints(*p1, *p2, segment=True)
group.draw(line, hwidth=0.2, fill='white')
for x, y in points:
p = hyper.Point.fromEuclid(x, y)
group.draw(hyper.Circle.fromCenterRadius(p, 0.1),
fill='green')
redraw(click_list)
# Create interactive widget and register mouse events
widget = DrawingWidget(d)
@widget.mousedown
def mousedown(widget, x, y, info):
if (x**2 + y**2) ** 0.5 + 1e-5 < 1:
click_list.append((x, y))
redraw(click_list)
widget.refresh()
@widget.mousemove
def mousemove(widget, x, y, info):
if (x**2 + y**2) ** 0.5 + 1e-5 < 1:
redraw(click_list + [(x, y)])
widget.refresh()
widget
Python动画
将drawSvg 导入为 绘图
# 绘制动画的一帧
def draw_frame ( t ):
d = draw .